TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD (TDH) is the TOTAL AMOUNT OF PRESSURE when water is flowing in a system.
in other words, TDH is the total equivalent height that a fluid is to be pumped, taking into account friction losses in the pipe.
It is comprised of 1) VERTICAL RISE AND FRICTION LOSS.
To determine the correct pump for your requirement, its important to calculate vertical rise and friction loss accurately.
To calculate Total Dynamic Head (TDH), we need to calculate the following:
A) Vertical Rise.
B) Friction Losses of all the pipes and components the liquid encounters on the discharge of pump.
C) After calculating both, add them together to calculate TDH.
For the purpose of easy understanding, we can assume the Total Dynamic Head for 25 GPM (gallons per minute )
to go from the Pump to Tank B in the example below.
How to Calculate Vertical Rise
A) Vertical Rise. Calculation of vertical rise is taken from the liquid’s starting point to its ending point.
As the liquid level in the tank decreases, the vertical rise will increase, and consequently, the total dynamic head will increase.
To simplify matters, let us take the below example assuming that the tank is empty .
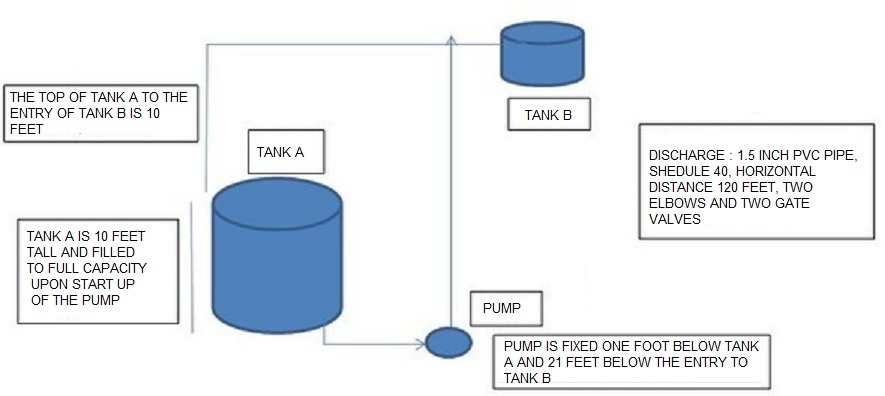
If the Tank A is full and the liquid is going to the top of Tank B, the vertical rise is 10 feet.
( Distance from the top of Tank A to the top level of Tank B )
If Tank A is half empty and there is only 5 feet of liquid available, then the vertical rise is 15 feet.
(distance from the liquids top level in Tank A to the top level of tank B )
If tank A is fully empty, then the vertical rise will be 21 feet.
(distance from the bottom level in Tank A to the top level of tank B )
With the vertical rise being anywhere from 10-21 feet, it is advisable to use 21 feet for calculation for safety
How to Calculate Friction Loss
B) Friction Loss. To calculate the friction loss you first need to know
1- Your desired flow rate as each rate will have a different friction loss.
The more flow going thru a pipe, the more friction loss there will be.
2- Type of pipe you are using, the schedule of the pipe, and the length of the pipe, both vertically and horizontally.
You also need to know how many elbows, T connectors, valves and anything else that comes into contact with the liquid.
Using the above example, let’s calculate the friction loss for 25GPM.
In this example:
There is 1.5 inch PVC Schedule 40 pipe.
The horizontal pipe distance from the pump to Tank B is 120 feet and the vertical pipe distance from the pump to the tank B is 21 feet.
There are 2 90 degree long radius elbows and 2 gate valves.
Once this information is calculated, take the following steps:
Step 1) Add the horizontal and vertical discharge pipe together.
120 feet+21 feet= 141 feet
Step 2) Go to this website: http://www.freecalc.com/fricfram.htm
Step 3) Enter pipe size, pipe schedule, piping material, piping length, valves, and fittings.
1.5 Inch, Schedule 40, PVC Material, 141 Piping Length in Feet, 2 90 LR Elbows, and 2 Gate Valves.
Step 4) Press “Calculate Pressure Drop.” After pressing “Calculate Pressure Drop,” the calculator states the friction loss as 5.6 feet.
you can also use this link for Total Dynamic Head calculation : https://www.pumpworld.com/total-dynamic-head-calculator.htm
The Result : Total Dynamic Head Calculation
Other Considerations When Calculating Total Dynamic Head
Other factors which can affect the friction loss include specific gravity, viscosity and temperature.
The more information you have on the system, the more accurate your friction loss number and by extension your Total Dynamic Head will become.
A liquid's specific gravity can change the friction losses slightly.
If the specific gravity is between 1.0 and 2.0 (water is 1.0), it is not necessary to use that information in your calculations.
If it is less than 1.0 or more than 2.0, it is suggested to use an online calculator.
Viscosity on the other hand can greatly increase friction losses.
If the liquid is viscous, determine the viscosity by either using a viscous specific gravity chart or an online viscous specific gravity calculator.
TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD OF A PUMP - CALCULATION
- Brand: GreenAge
- Product Code: 3233
- Availability: In Stock
-
Rs.0/-
- Ex Tax: Rs.0/-
Related Products
TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD OF A PUMP - CALCULATION
TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD (TDH) is the TOTAL AMOUNT OF PRESSURE when water is flowing in a system.in o..
Rs.0/- Ex Tax: Rs.0/-
TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD OF A PUMP - CALCULATION -2
CALCULATION OF TOTAL DYNAMIC HEAD - METHOD 2Assume that the land is a slop and the pump is installed..
Rs.0/- Ex Tax: Rs.0/-
SPRINKLER INSTALLATION - CALCULATION
To calculate the pressure required for different quantity or models of sprinklers, please first..
Rs.0/- Ex Tax: Rs.0/-
Tags: vertical height